NTFS File System
NTFS, an acronym that stands for New Technology File System, is a file system first introduced by Microsoft in 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1.
It is the primary
file system used in Microsoft's Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7,
Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000, and Windows NT operating systems.
The Windows
Server line of operating systems also primarily use NTFS. It is also compatible
with other operating systems such as Linux and BSD. macOS provides read-only support
for NTFS.
Note: NTFS stands for other terms as well, but none of them have anything to do with what is being discussed on this page. These include not trusted for servers, never tested file system, new tools for storage, and no time for social.
How to See If a Drive is Formatted as NTFS
There are several
ways to check if a hard drive is formatted with NTFS or uses a different file
system.
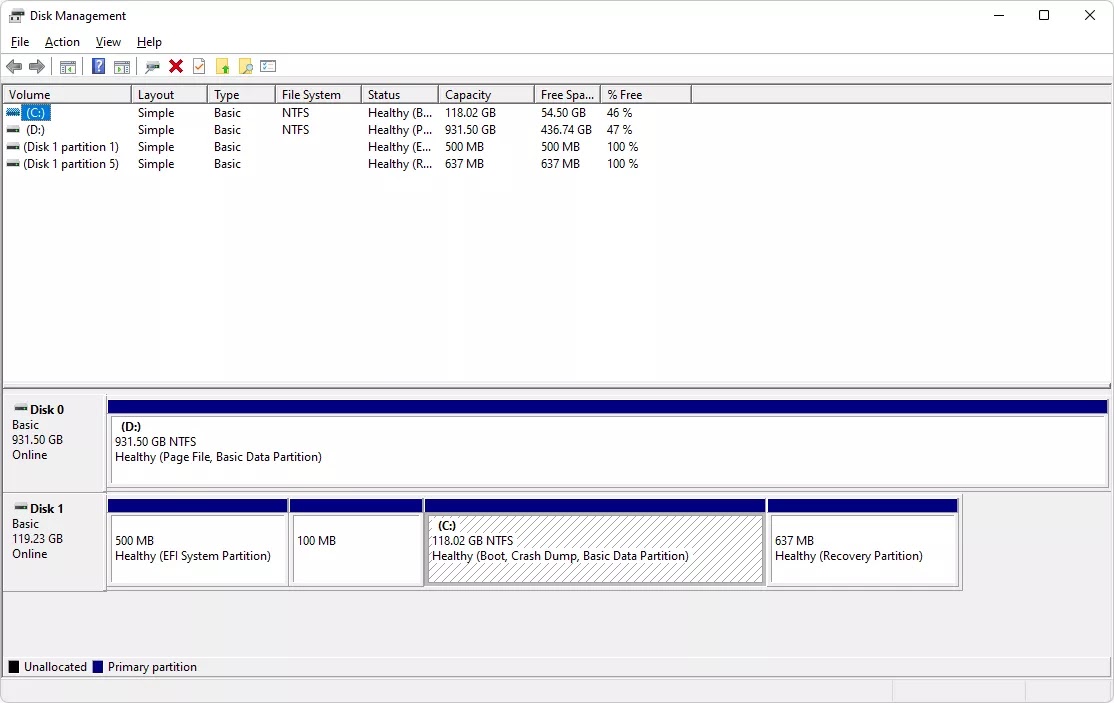
Use Disk Management
The first and
probably the easiest way to view the status of a drive or drives is to use Disk
Management.
The file system
is listed here along with the volume and other details about the drive.
Open File Explorer
Another way to check if a drive has been formatted with the NTFS file system is to right-click or long-press on the drive in question directly in File Explorer.
Then select Properties from the dropdown menu. Read what's next to "File System" on the "General" tab. If the drive is NTFS, it will be File System: NTFS.
Enter a Command Prompt
Yet another way to see what file system a hard drive is using from the command line interface.
Open a command prompt (may need to be an
elevated command prompt on some versions of Windows) or Windows Terminal and
type this to see various details about the C: drive, including its file system:
fsutil fsinfo volumeinfo C:Tip: Use the command fsutil fsinfo volumeinfo C: | findstr "system" to truncate the results and display only the file system.
To check another
disk, use the drive letter instead of C:. If you don't know the drive letter,
use the fsutil fsinfo drives command to get a printout to the screen.
Features of NTFS
In theory, NTFS
can support hard drives up to just under 16 EB. Individual file size is limited
to just under 256TB, at least on Windows 8, 10, and 11 and some newer versions
of Windows Server.
NTFS supports
disk usage quotas. An administrator sets these quotas to limit the amount of
disk space a user can use. It is mainly used to control the amount of shared
space that someone can use, usually on a network drive. You can check free disk
space without using disk usage quotas.
File attributes
that were previously not visible on Windows operating systems, such as the
compressed attribute and the indexed attribute, are available with
NTFS-formatted drives.
File system
encryption is another feature supported by NTFS. EFS offers file-level
encryption, which means individual files and folders can be encrypted. This is
a different feature than full disk encryption, which is the encryption of an
entire disk (like what you see in these disk encryption programs).
NTFS is a journal
file system; provides a way to write system changes to a log or journal
before the changes are actually written. This feature allows the file system to
return to previously well-performing conditions when it fails because new
changes have not yet been committed.
Volume Shadow
Copy Service is a feature of NTFS used by online backup utilities and other
backup software tools to make backup copies of files currently in use, as well
as by Windows itself to store copies of security of your files.
Another feature
introduced in this file system is called transactional NTFS. This allows
software developers to create applications that either completely succeed or
completely fail. Programs that exploit this don't run the risk of applying some
changes that work and some that don't, a recipe for serious trouble.
Transactional NTFS is a fascinating subject; You can read more about it in
these Wikipedia and Microsoft articles.
NTFS also
includes other features, such as B. hard links, sparse files, and reparse
points.
NTFS Alternatives
FAT was the
primary file system on older Microsoft operating systems and was largely
superseded by NTFS. However, all versions of Windows still support FAT, and
it's common to find drives formatted with it instead of NTFS.
The exFAT file
system is a newer file system, but it was designed to be used where NTFS
doesn't work well, such as B. on flash drives. Some differences between NTFS
and exFAT include fewer files per directory in the latter file system but much
larger disk sizes than in the former.





Comments
Post a Comment